

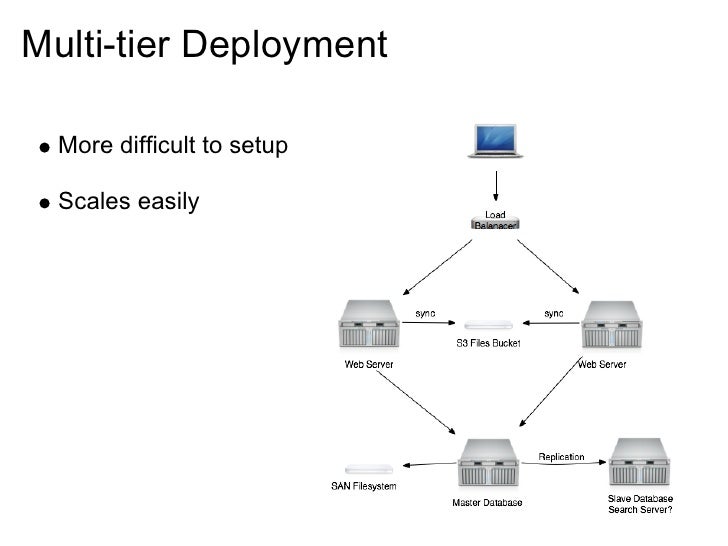
We solved this by setting up a separate Docker image using the same Drupal application, which we can run in a Fargate service. If you ever worked with Drupal you probably used Drush commands and it’s almost inevitable to use cronjobs. Using this setup we ensure that state is kept in services like ElastiCache and RDS, so the application can scale in and out without losing any data. All static files are stored in S3, which we achieved using the Drupal module S3 File System.The database is migrated to AWS Aurora.For now we migrated it to an EC2 instance, but we have plans to make it scalable later on. The existing frontend also relies on this component. As a search engine we use SOLR, because of its great performance and the available Drupal module.For caching we use AWS ElastiCache with a Redis engine as a backend.The other components are also migrated to AWS making use of the services AWS offers as much as possible: If the CPU or memory exceeds a certain threshold we scale out automatically and after a cooling down period, we scale back in. Both run in a task within the Fargate service, which we configured for autoscaling. Our setup uses 2 containers, one for Nginx and one for PHP-FPM. Of course only after it ran successfully through our CI/CD pipeline. By using Docker images, we can use the same configuration for development on our local machines as for running the application on production. We configured it to use an Application Load balancer (ALB) to distribute traffic evenly across the tasks in our service. We started of by decoupling all components and ended with the following architecture, where we can scale out (and scale in) on component level: Backend Architectureįor the Drupal application itself we choose for the AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) using Fargate. Therefore, also the Drupal backend also needed to be migrated to the new infrastructure in AWS.
This was partially fixed by caching in the frontend application, but as this is a legacy application which is being rebuilt as we speak, this isn’t optimal.Īs mentioned the entire application is currently being rebuilt and all new components will be hosted in AWS. The only possibility was to scale vertically, while ideally, you would scale horizontally.Īs a consequence the frontend application, serving thousands of visitors a day, suffered poor backend performance.

The main reason the existing solution was underperforming was because all components (Nginx, MariaDB, SOLR, Redis) were all running on one VPS. For this project, Drupal was merely used as backend and queried by a frontend application through the JSON API, as well as for assets like images and static JSON files. Our goal was to develop a scalable solution and consolidate all components of the platform in the same infrastructure. All static files should have your CNAME in URLs.We faced the challenge of migrating a Drupal application from a VPS, which was under constant high load and thus underperforming, to AWS. To do that press F12 or open Developers Tools in your browser, choose the Network tab and refresh the page.
#Drupal aws s3 code#
Integration has been completed! We highly recommend you to check the HTML code of your web page to ensure that URLs have been rewritten properly from your original ones to CNAME from the control panel. These steps are needed if you are going to deliver your CDN content via HTTPS. Choose the Other tab on the right of the CDN Module configuration screen. Scroll down and choose Far Future expiration, then click Save Configuration. Choose Enable and Save configuration.Ĭhange the CDN module status to Enabled and save the setting by hitting the Save Configuration button.Ĭhoose the "Details" tab on the right of the screen.įor the Mode choose Origin Pull and enter CNAME specified in the Gcore Control panel.Įnsure that your CNAME record has been configured in a proper way before using it for integration. If the installation was successful, you will see the following.Īs soon as the CDN Module is successfully installed, get back to the modules list and scroll down to CDN.
#Drupal aws s3 install#
Upload CDN Module from your browser and install it. If you manually changed CMS patterns, the plugin might not help you.Ĭhoose Modules in your Administration bar on top of the page.Īs soon as you have downloaded CDN Module from, choose Install new module and download. The plugin works only with default CMS pattern. Before you take any steps please back up your files and database.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
